The transportation sector is still among the main sources of air pollution and climate change on Earth, accounting for approximately 59% of oil consumption and 22% of CO2 emissions. Identifying effective strategies to limit the fuel consumed by vehicles could thus contribute to reducing pollution while also addressing global energy shortages.
Researchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology recently set out to tackle this challenge using a reinforcement learning–based computational model.
This model, outlined in a paper posted to the preprint server arXiv, is designed to optimize fuel consumption in car-following scenarios, specifically in situations in which semi-automated and autonomous vehicles are driving in proximity and need to maintain a safe distance from each other by adjusting their speed.
“The inspiration for this paper arose from the increasing demand for sustainable and energy-efficient transportation solutions,” Hui Zhong, co-author of the paper, told Tech Xplore. “With traffic congestion and inefficient driving behaviors significantly contributing to fuel consumption and emissions, we sought to explore ways to mitigate these challenges.”
The main objective of this recent work by Zhong and his colleagues was to develop a computational model that would optimize fuel consumption in car-following scenarios, while ensuring that cars retain a safe distance from each other and traffic flows efficiently. The model they developed, dubbed EcoFollower, is based on deep reinforcement learning.

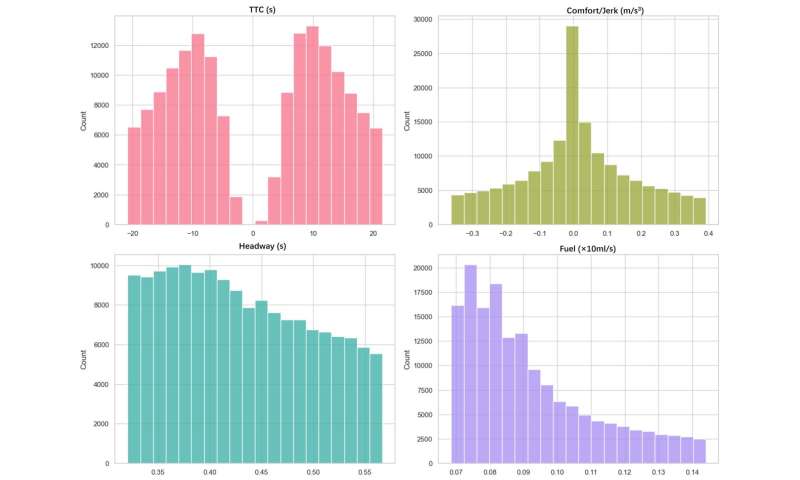
Descriptive analysis of four key indicators. Credit: Zhong et al. 
Test results for safety, comfort, efficiency, and fuel consumption in the EcoFollower model. Credit: Zhong et al.
“EcoFollower is a car-following model based on reinforcement learning, designed to optimize fuel consumption during driving,” Zhong explained. “The model continuously learns from its environment, adjusting following distances and acceleration patterns to achieve the most fuel-efficient driving behavior. What sets EcoFollower apart is its ability to balance fuel efficiency with maintaining safe and smooth traffic flow.”
Conventional models to optimize the operation of vehicles in car-following scenarios typically only focus on safety or aim to facilitate the efficient flow of traffic. The EcoFollower model, on the other hand, is designed to also reduce fuel consumption.
The researchers evaluated their model in a series of tests where they applied it to the Next Generation Simulation (NGSIM) dataset. This is an open-source collection of traffic data collected at four different locations. The results of the team’s initial tests were highly promising, as EcoFollower was found to significantly reduce fuel consumption in all the scenarios it was tested on.
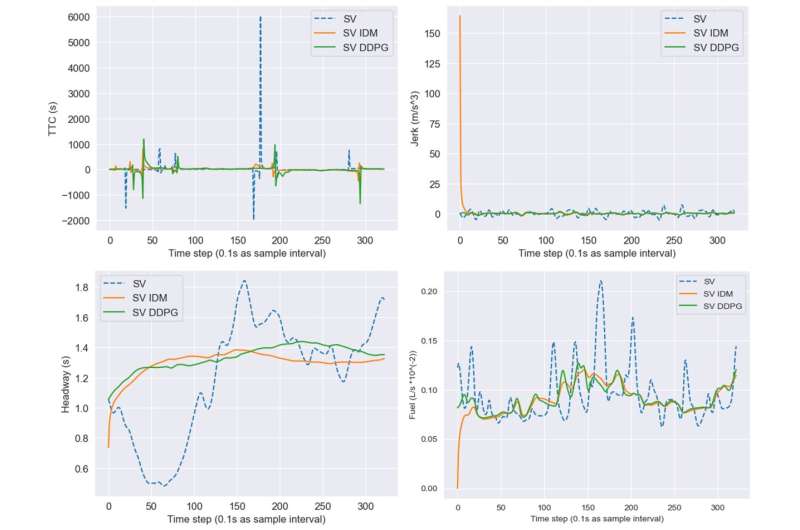
“We demonstrated that reinforcement learning can be effectively applied to real-world driving scenarios to reduce fuel consumption,” said Zhong. “Our experiments showed that EcoFollower could lower fuel consumption by 10.42% compared to actual driving scenarios. This result has significant implications for reducing overall emissions and promoting sustainable transportation.”
In the future, the EcoFollower model could be integrated into advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving systems, helping to boost their efficiency and reduce their environmental impact. Meanwhile, the researchers plan to continue working on the model to further improve its performance.
“While it already performs better than traditional Intelligent Driver Mode(IDM) and reduces fuel consumption by 10.42% compared to actual driving scenarios, more scenarios and datasets are needed to further test and enhance its generalization and robustness,” added Zhong. “For instance, in a mixed-autonomy traffic environment, the behavior of human-driven vehicles differs from that of autonomous vehicles, which could impact the model’s performance.”
More information:
Hui Zhong et al, EcoFollower: An Environment-Friendly Car Following Model Considering Fuel Consumption, arXiv (2024). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2408.03950
© 2024 Science X Network
Car-following model based on reinforcement learning could cut fuel consumption (2024, September 5)
retrieved 5 September 2024
from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-09-car-based-fuel-consumption.html
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.