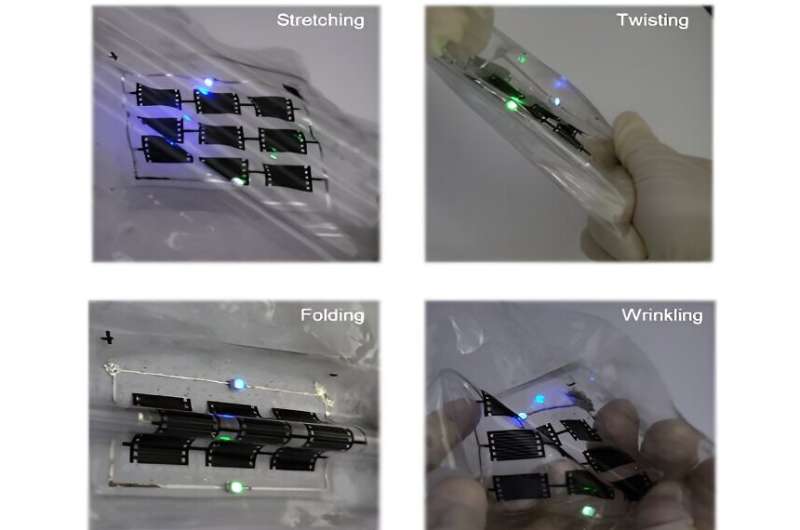
Researchers have achieved a significant breakthrough in developing a small-scale energy storage device capable of stretching, twisting, folding, and wrinkling. Their study is published in the journal npj Flexible Electronics.
The advent of wearable technology has brought with it a pressing need for energy storage solutions that can keep pace with the flexibility and stretchability of soft electronic devices. Micro supercapacitors (MSCs) have emerged as a promising candidate for deformable energy storage, due to high-power density, rapid charging, and long cycle life.
However, the fabrication of interdigitated electrode patterns capable of maintaining the energy storage performance under repeated stretching and twisting has remained a great challenge, because brittle materials like gold (Au) have been commonly used as an electrode. Meanwhile, though eutectic gallium-indium liquid metal (EGaIn) has high conductivity and deformability, a fine patterning of EGaIn is extremely difficult due to very high surface tension of EGaIn.
The research team successfully fabricated fine patterning, by using laser, of both EGaIn and graphene (serving as an active material) layers as on a stretchable polystyrene-block-poly(ethylene-co-butylene)-block-polystyrene copolymer (SEBS) substrate.
During laser ablation of EGaIn and graphene layers, the underlying stretchable SEBS substrate was not damaged, which maintained the flexibility of MSC device. The areal capacitance of the resulting MSC retains its original value even after stretching up to 1,000 cycles. Also, the fabricated MSCs operate stably under various mechanical deformations, including stretching, folding, twisting, and wrinkling.
The research team included Professor Jin Kon Kim and Dr. Keon-Woo Kim from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), in collaboration with Dr. Chanwoo Yang and Researcher Seong Ju Park from the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (KITECH).
Professor Jin Kon Kim said, “The use of laser-patterned liquid metal electrodes represents a significant step forward in the development of truly deformable energy storage solutions. As wearable technologies continue to advance, innovations like these will play a vital role in ensuring that our devices can adapt to the demands of our dynamic lifestyles.”
More information:
Keon-Woo Kim et al, Deformable micro-supercapacitor fabricated via laser ablation patterning of Graphene/liquid metal, npj Flexible Electronics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41528-024-00306-2
Pohang University of Science and Technology
Rubber-like stretchable energy storage device fabricated with laser precision (2024, April 24)
retrieved 26 April 2024
from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-04-rubber-stretchable-energy-storage-device.html
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

Researchers have achieved a significant breakthrough in developing a small-scale energy storage device capable of stretching, twisting, folding, and wrinkling. Their study is published in the journal npj Flexible Electronics.
The advent of wearable technology has brought with it a pressing need for energy storage solutions that can keep pace with the flexibility and stretchability of soft electronic devices. Micro supercapacitors (MSCs) have emerged as a promising candidate for deformable energy storage, due to high-power density, rapid charging, and long cycle life.
However, the fabrication of interdigitated electrode patterns capable of maintaining the energy storage performance under repeated stretching and twisting has remained a great challenge, because brittle materials like gold (Au) have been commonly used as an electrode. Meanwhile, though eutectic gallium-indium liquid metal (EGaIn) has high conductivity and deformability, a fine patterning of EGaIn is extremely difficult due to very high surface tension of EGaIn.
The research team successfully fabricated fine patterning, by using laser, of both EGaIn and graphene (serving as an active material) layers as on a stretchable polystyrene-block-poly(ethylene-co-butylene)-block-polystyrene copolymer (SEBS) substrate.
During laser ablation of EGaIn and graphene layers, the underlying stretchable SEBS substrate was not damaged, which maintained the flexibility of MSC device. The areal capacitance of the resulting MSC retains its original value even after stretching up to 1,000 cycles. Also, the fabricated MSCs operate stably under various mechanical deformations, including stretching, folding, twisting, and wrinkling.
The research team included Professor Jin Kon Kim and Dr. Keon-Woo Kim from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), in collaboration with Dr. Chanwoo Yang and Researcher Seong Ju Park from the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (KITECH).
Professor Jin Kon Kim said, “The use of laser-patterned liquid metal electrodes represents a significant step forward in the development of truly deformable energy storage solutions. As wearable technologies continue to advance, innovations like these will play a vital role in ensuring that our devices can adapt to the demands of our dynamic lifestyles.”
More information:
Keon-Woo Kim et al, Deformable micro-supercapacitor fabricated via laser ablation patterning of Graphene/liquid metal, npj Flexible Electronics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41528-024-00306-2
Pohang University of Science and Technology
Rubber-like stretchable energy storage device fabricated with laser precision (2024, April 24)
retrieved 26 April 2024
from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-04-rubber-stretchable-energy-storage-device.html
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.








